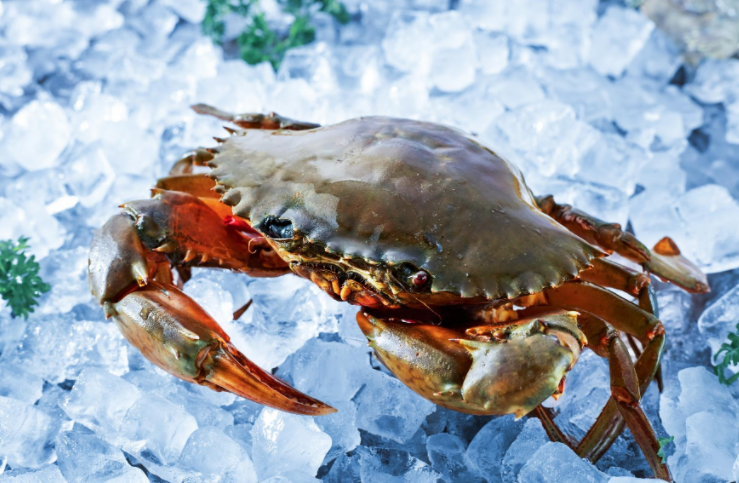
Scylla serrata, also known as mantis crab, mantis crab, blue crab, yellow crab, is an animal of the genus Scylla in the family Portunidae.

01 History of Zoology
The mud crab is named because its carapace is green and the side teeth on the front edge are like saw teeth
02 Habitat
The mud crab lives in shallow seas and intertidal zones (i.e., tidal flats that are submerged during high tide and exposed during low tide). It mostly lives in muddy bottoms and places with seaweed and depressions, where there is still water after low tide, as well as near the roots of mangroves and shallow sea reef caves or other shelters.
The mud crab has a wide range of adaptability to salinity and can grow in seawater with a salinity of 5-32%, with an optimal salinity of 12-16%. The distribution area of mud crabs is different, and the range of water temperature adaptation is also different. The most suitable water temperature for the growth of mud crabs in Shanghai, Jiangsu and northern Guangdong is 18-25°C; in the coastal area of Guangxi, China, mud crabs grow normally at 18-30°C, and the most suitable water temperature is 20-26°C.
03 Distribution range
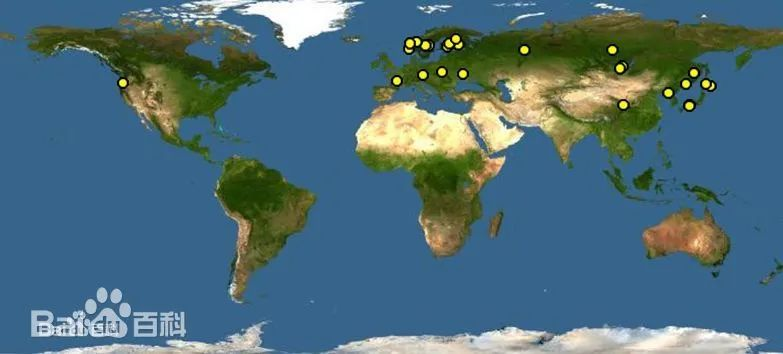
Mud crabs are widely distributed in tropical and subtropical waters from India to the western Pacific, including the southeast coast of China, Bangladesh, Japan, Vietnam, Thailand, the Philippines, Indonesia, Hawaii, Australia, New Zealand and southeast Africa.
The factory of Rishifu mud crabs is located in the natural mangrove area of Bangladesh World Heritage
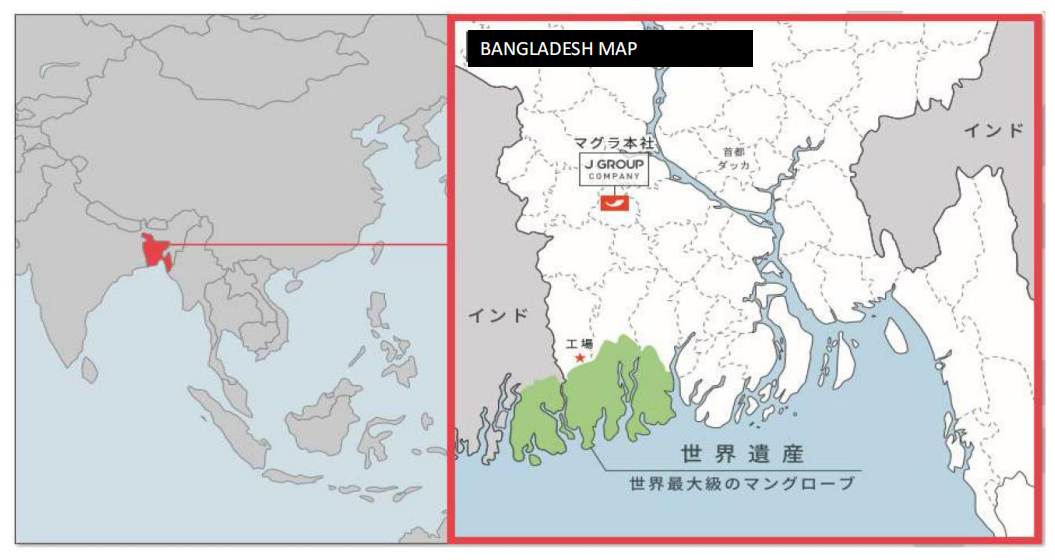
Rishifu aquaculture farm covers an area of 11.6 hectares, only uses natural bait, does not use any drugs, and adopts an environmentally friendly breeding model.
(The feed comes from the "natural small fish and shrimp" in the mangroves, the habitat of the crabs. The breeders will put the feed into the breeding barrels one by one)

Provide customers with safe, reliable and high-quality products. The farm is close to the processing plant, which can directly process the freshest raw materials and maximize the freshness of the raw materials. A farm will have three permanent employees who monitor in shifts 24 hours a day.

04 Main value
a. Economic value
In addition to fresh food, it can also be canned. The shell of the mud crab can be made into soluble chitin after chemical treatment such as decalcification, degreasing, bleaching and deacetylating. The solution has a high viscosity and can be diluted with water in any proportion without precipitation. Soluble chitin is widely used and has excellent performance. It is not only used in textiles, printing and dyeing, artificial fibers, papermaking, wood processing, plastics and other industries, but also in medicine, seasoning and other aspects, becoming a widely used industrial raw material.
b. Edible value
The mud crab is relatively large, generally weighing 0.2-0.5 kg, and can reach more than 2 kg. It has tender meat and delicious taste, making it an excellent edible crab.
c. Nutritional value
The components of the mud crab are rich in protein, of which the female gonads contain up to 30.98%, the highest protein content among fresh products. The protein amino acids of the mud crab are complete, and the essential amino acid score is 84.23-93.58.
The body of the mud crab is rich in fat and unsaturated fatty acids (UFA). The UFA of the muscle is 74.58%, which is higher than the 65.61% of the swimming crab* muscle and 74.3% of the mantis shrimp head. The polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) are as high as 47.83%, which is nearly 10% higher than the 38.43% of the swimming crab and slightly lower than the 51.5% of the mantis shrimp head; EPA is as high as 18.04%, DHA is 13.52%, which is comparable to the 15.21%, 17.69% of the swimming crab, 15.75%, 13.96% of the mantis shrimp head and commercially available deep-sea fish oil products. The UFA of the female gonad is also as high as 70.30%, the UFA of the male gonad is 62.48%, and the lowest liver UFA is 58.32%, all of which are higher than the swimming crab. Saw-edged mud crab has high content of unsaturated fat, especially high content of w-3 fatty acids EPA and DHA which cannot be synthesized in the human body.
Saw-edged mud crab is a high potassium and low sodium food, so it is more suitable for patients with hypertension. Its liver calcium content is extremely high, second only to stone snail, dace, dried shrimp, dried shrimp and anchovy +, and the natural organic calcium is easy for human body to digest and absorb. The content of other essential elements such as magnesium, iron, copper, zinc, and manganese in saw-edged mud crab is also high. The selenium content of each component of saw-edged mud crab is very high, especially the female gonad.
d. Medicinal value
Saw-edged mud crab has medicinal value. Crab meat clears heat and disperses blood, nourishes tendons and replenishes qi, and can treat tendon and bone damage, scabies, lacquer sores, and burns; crab claws break blood and eliminate accumulation, and can treat postpartum abdominal pain; crab shell attacks poison and removes blood stasis, and can treat blood stasis, breast pain, and frostbite.
05 Morphological characteristics
The cephalothorax is oval, with a raised and smooth back, and is named for its green body color. There is an obvious "H"-shaped indentation in the stomach and heart area of the cephalothorax, and a thin and interrupted horizontal granular protrusion in the stomach area. The front edge is shorter than the rear edge, and there are 9 teeth of equal size. There are 4 teeth on the forehead, and the inner eye socket teeth are larger than the forehead teeth. The whole foot is thick and slightly asymmetrical, with 3 spines on the front edge of the long segment and 2 spines on the rear edge; the palm is swollen, and there are blunt teeth on the inner edge of the two fingers. The edges of the first three pairs of walking leg joints have brush-like hairs, and the fingers and palms of the last pair of walking legs are flat and paddle-shaped, and they are good at swimming. The abdomen of the male is wide triangular, and the abdomen of the female is round.
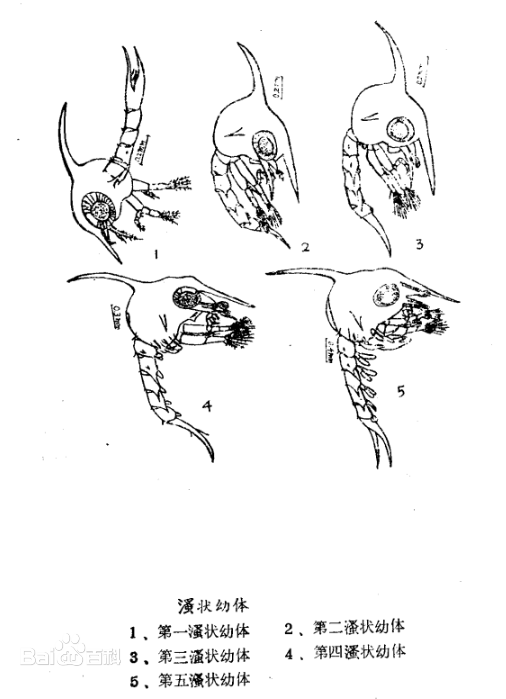
a. Daphnia larvae
The pan-shaped larvae are triangular and divided into the cephalothorax and abdomen. The cephalothorax has one frontal spine, one dorsal spine, and a pair of lateral spines. The abdomen has spines. The spines have the effect of enhancing floating.
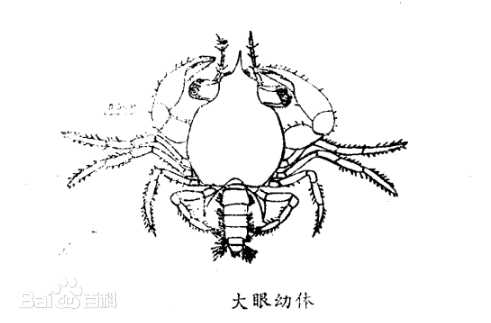
b. Megalopa
The cephalothorax of Megalopa larvae is 8.2 mm long, 1.8 mm wide, and 1.5 mm long. The body is relatively flat dorsally and ventrally, and is crab-like in shape, but its abdomen has not yet bent under the cephalothorax. It has 5 pairs of well-developed abdominal limbs, which are swimming organs. This is a transitional type from planktonic to benthic life. The megalopa has a pair of large compound eyes, which are attached to the end of long eye stalks that are exposed outside the eye sockets.
C. Adult crab
The whole body of the mud crab is divided into the cephalothorax and abdomen. The cephalothorax is completely healed, and the abdomen is extremely degenerate and folded in the ventral groove inside the ventral sternum of the cephalothorax.
(a) Cephalothorax
The cephalothorax of the mud crab is wide, with a large cephalothorax on its back. The back of the cephalothorax is greenish-blue, and the ventral side is grayish-white. The overall shape is slightly horizontally oval. The entire carapace is composed of chitin and calcium, which protects the soft tissue inside the body. The forehead is in the middle of the front edge of the cephalothorax. There are 6 tooth processes in front of the forehead, which are called forehead teeth. Below the forehead is the mouth part of the mouth frame. The mouth part is composed of 6 pairs of bipedal appendages, namely 1 pair of mandibles, 1 pair of first maxillae, 1 pair of second maxillae, and 3 pairs of maxillopods, which are arranged in layers from the inside to the outside, like 6 screen doors. Food must pass through these 6 doors to enter the esophagus. The inner limbs of the mandibles are well developed and are in the shape of molars. The mandibles are thin. The first maxillopod has a radial plate and can move independently. There is a pair of compound eyes with eye stalks on the two sides of the six tooth processes in the forehead. The eye stalks have a large range of movement and can swing left and right. They usually lie horizontally in the eye sockets. When frightened, they stand up and let the compound eyes show outside. There is a pair of large and small antennae inside the compound eyes. The antennae are bipedal, and there is an excretion hole at the base of the antennae for excreting urine. There are 9 tooth processes on the front edges of both sides of the eye sockets, which are called lateral teeth. The ninth tooth process at both ends is blunt and oblique upward, unlike the swimming crab which is horizontal and sharp. The serrata has 5 pairs of appendages between the cephalothorax and the thoracic carapace, extending horizontally on both sides. The first pair is particularly powerful, with large palm segments, no hair, and serrations in the knuckles of the whole foot. The second, third, and fourth pairs of appendages are claw-like walking legs at the tip of the last segment, used for walking. The last pair of appendages is flat and folded like a foliage, with bristles on the front and back edges, called swimming legs.
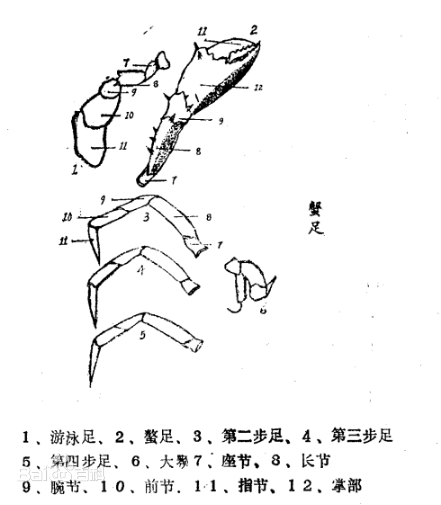
(b) Abdomen
The abdomen of the serrata is flat, commonly known as the crab navel, and is divided into 7 segments, bending from the back to the front, close to the back of the cephalothorax. The crab navel is on the ventral groove of the thorax. The shape of the navel of male crabs is different from that of female crabs. The shape of the navel of male crabs is narrow and long, triangular, commonly known as "pointed navel"; the shape of female crabs is wide and flat, blunt and round, commonly known as "round navel". This is the most obvious sign to distinguish the sex of male and female crabs from the outside. The abdomen of the crab is attached with ventral limbs, and the number and shape of ventral limbs vary according to the sex of the crab. The ventral limbs of male crabs are degenerate, with only two pairs of sharp appendages made of calcium, which are attached to the first and second abdominal segments. Each ventral limb has only an inner limb, which has been transformed into a copulatory organ for sperm delivery during mating. There are four pairs of ventral limbs on the inner side of the abdomen of female crabs, all of which are bilimbed, divided into inner limbs and outer limbs, with bristles on them to attach eggs during spawning and become part of the reproductive organs. Female crabs have two genital pores, located in the middle of the ventral groove opposite the base of the third pair of walking legs.
OUR MISSION
Provide high-quality services and products to customers
/ Hotline /
021-34505035 (Shanghai)
/ Business consultation /
Li Cheng 13661660483
Zhou Cheng 18621585930
/ Official website /
https://www.rsftrading.com/

COMPANY TEL
021-3450-5035
E-MAIL
917935736@qq.com
COMPANY ADDRESS
Room 403, No. 5, Lane 72, Haowen Road, Minhang District, Shanghai
All Rights Reserved © Copyright 2021 Shanghai Rishifu Trading Co., Ltd.
Website:OCEAN